Tympanic Membrane Repair and Hearing Restoration (Tympanoplasty)
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to repair perforations or tears in the eardrum.
Take the First Step Now
For more information, contact us
Schedule your appointment or online consultation with Prof. Dr. Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz now. Take the first step in your treatment process and let’s begin your journey to recovery together with personalized solutions.
What is Tympanoplasty?
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to repair perforations or tears in the eardrum (tympanic membrane). This surgery is performed on individuals with a persistent hole or tear in the eardrum to correct hearing loss and prevent recurrent ear infections.
Common Purposes of Tympanoplasty:
- Eardrum Repair: A hole or tear in the eardrum can lead to hearing loss and increase the risk of infection. Tympanoplasty repairs this perforation, restoring the normal function of the eardrum.
- Hearing Improvement: Repairing the eardrum helps restore sound transmission to the hearing bones in the middle ear, aiding in correcting hearing loss.
- Prevention of Infections: A hole in the eardrum allows bacteria to enter the middle ear, causing infections. Tympanoplasty closes this hole, reducing the risk of infection.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon uses tissue from another part of the body (typically fascia tissue) to close the eardrum hole. The procedure is generally successful, and most patients regain normal hearing function after the recovery process.
Candidates for Tympanoplasty
- Individuals with Chronic Ear Infections: Recurring or prolonged ear infections can cause the eardrum to tear, making tympanoplasty necessary.
- People with Perforated or Torn Eardrums: Individuals whose eardrums are perforated or torn due to injury, infection, or other reasons may undergo tympanoplasty to correct hearing loss and reduce infection risk.
- Those with Hearing Loss: Structural issues in the eardrum or middle ear may cause hearing loss, and tympanoplasty can be performed to address this loss.
- Individuals with Chronic Otitis Media: Those experiencing persistent fluid buildup or chronic inflammation in the middle ear may be candidates for tympanoplasty to repair the damage caused by these conditions.
- Patients with Middle Ear Ossicle Damage: When the ossicles (hearing bones) in the middle ear are damaged or not functioning, tympanoplasty can be performed to address these issues.
How is Tympanoplasty Performed?
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to repair holes or tears in the eardrum. The general steps are as follows:
Pre-Surgical Preparation:
- Evaluation and Planning: Before surgery, the doctor performs hearing tests to assess the extent of eardrum damage and any other possible issues in the middle ear.
- Anesthesia: The procedure is generally performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully asleep during surgery. In some cases, local anesthesia may be used.
Surgical Stages:
1. Surgical Access
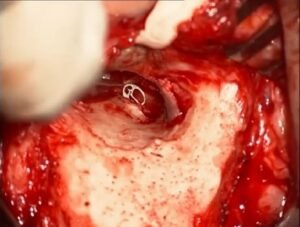
- The surgeon usually makes an incision either through the ear canal or behind the ear to reach the eardrum.
- An incision through the ear canal provides direct access to the eardrum for a minimally invasive approach.
- An incision behind the ear creates a larger surgical field, allowing the surgeon to access the ossicles if needed.
2. Eardrum Repair:
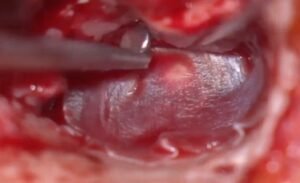
- The surgeon typically uses a thin layer of tissue taken from another part of the body (usually fascia tissue) to cover the hole in the eardrum.
- Once the tissue is in place, gelatin sponges or absorbable materials may be used to support the repair and hold it in position.
3. Procedures in the Middle Ear:
- If necessary, the surgeon can adjust or repair the ossicles to improve sound transmission to the inner ear.
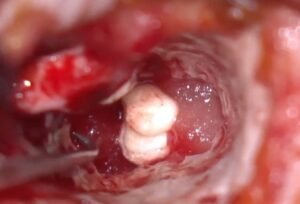
4. Closure and Dressing
- At the end of the surgery, a protective dressing or packing is placed in the ear canal to help secure the tissue graft during healing.
- If an incision was made behind the ear, it is closed with stitches.
Post-Surgery:
- Recovery Process: After surgery, a feeling of fullness, mild pain, or dizziness in the ear is common. These symptoms generally diminish within a few days.
- Packing Removal: The packing in the ear canal is usually removed about one week post-surgery.
- Hearing Evaluation: A few weeks after surgery, hearing tests are performed to evaluate the success of the operation.
Tympanoplasty aids in restoring hearing by repairing the eardrum and preventing recurrent ear infections. The success rate of the procedure is high, though, as with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications. Therefore, discussing all details and possible outcomes with your doctor before surgery is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions About Eardrum Repair and Hearing Restoration (Tympanoplasty):
How long does the surgery take?
Tympanoplasty usually takes 1-2 hours, though the duration can vary depending on the surgeon’s technique and the size of the perforation.
What should I expect after the surgery?
After surgery, a packing is placed in the ear canal, which is usually removed within a week. Mild pain, dizziness, or a feeling of fullness in the ear is normal during the recovery period.
When will my hearing improve after the surgery?
Hearing improvement typically begins a few weeks after surgery, but full recovery and hearing evaluation usually require waiting 2-3 months.
What are the risks of tympanoplasty?
As with any surgery, there are some risks associated with tympanoplasty, including infection, hearing loss, facial nerve damage, dizziness, and unsuccessful outcomes. However, these risks are generally low.
When can I return to my normal routine after tympanoplasty?
Most patients can resume light activities a few days after surgery. Full recovery takes about 2-4 weeks, during which strenuous physical activities should be avoided.
How should I protect my ear after tympanoplasty?
After surgery, avoid water in the ear to prevent infections. Use protective earplugs when bathing, and follow your doctor’s recommended ear care instructions.
Can tympanoplasty be repeated?
Nadiren, eğer kulak zarı tam olarak iyileşmez veya tekrar yırtılırsa ikinci bir timpanoplasti ameliyatı gerekebilir. Düzenli kontroller bu durumun tespit edilmesi için önemlidir.
Is dizziness normal after surgery?
Yes, dizziness is possible after surgery. It is usually temporary and decreases within a few days.
Is there a risk of infection after tympanoplasty?
There is a risk of infection after surgery, but following your doctor’s instructions for antibiotics and aftercare can help minimize this risk.
My paths crossed with Dr. Deniz because of my vocal cord polyp. My indecision before my doctor cost me 8 months. It didn't take us 8 minutes to get examined and decide on surgery. I pray for you for restoring my hoarse voice. I'm so glad Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz🙏
My nephew Ugur Karaer was suffering from empty nose syndrome. We went to every doctor in Istanbul. Finally, God brought us to Dr. Deniz. He performed the surgery successfully and saved my nephew's life. May God bless him.
I don't know how many surgeries I've had myself. But when it comes to children, everything calms down. 🙁 After seeing three doctors for my 2.5-year-old daughter's adenoid and tonsillectomy, we thankfully found Prof. Dr. Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz. His knowledge and patient approach made us believe he was by far the best doctor in this field. His assistant, secretary, the specialist who performed the hearing test... the entire team was extremely professional. Success is a team effort. That's why the whole process went smoothly, and we left satisfied. 💕 May God bless him 🙏🏻
We came from Almaty on vacation, and my son started having ear pain from the very first day. They recommended drops and medications, but nothing helped. We stumbled across a doctor online and decided to take a chance. She turned out to be wonderful, and after the first dose of medication, my son felt better. Within a week, there was no trace of the infection. Special thanks to the translator for her care, understanding, and professionalism.
I was suffering from empty nose syndrome. For those who don't know, I should say that almost all of my nasal tissue was removed. It is a very bad disease. I went to 100 ENT doctors in Istanbul and they couldn't find a solution. Finally, I found Deniz Hoca, who is an expert in this field, and he took cartilage from my rib and performed the surgery and I got better. Thank you very much for everything.
I had a tonsillectomy performed by our doctor, Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz. The surgery went smoothly, and although it's said to be more difficult for adults, I recovered very quickly. I'm so glad I chose Mustafa.
Hello, they told me that my parotid gland needed to be removed. I went to so many doctors that I finally decided on Dr. Mustafa. I am glad I chose Dr. Mustafa. You do not need to look for a doctor, you can choose my doctor with peace of mind without any worries.
I had a nose surgery 9 months ago by Mustafa Deniz Hoca. Both he and his team are always in touch with you before and after the surgery and provide detailed answers to questions. I am very pleased with my nose in terms of aesthetic appearance and health. Thank you and your entire team for everything.
First of all, I would like to thank my instructor Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz for his efforts. I had a nose surgery about 4 months ago. Like everyone else, I had the opportunity to research and compare the videos taken by many people who had this surgery and the perspectives of experts in their field on nose surgeries. I am very happy that I made the right decision and had surgery with my instructor Mustafa. I sincerely recommend my instructor Mustafa to everyone who wants to breathe both aesthetically and healthily and has problems.
I had a nose surgery in February. They never failed to show interest from the moment I entered the clinic until the last moment. No one even understands that I had plastic surgery. Mr. Deniz is one of the best in his field. I recommend it to everyone.
I had a nose surgery 3.5 months ago. The surgery and recovery process went great. There are a few things you should pay attention to after the surgery, they don't affect your quality of life too much. The doctor makes you feel very comfortable about that because it's not as complicated as you think. Other than that, I can breathe easily now, which is the most important thing. Also, Assistant Ayşegül Hanım gets back to you directly at any time of the day, no matter how long it has been since the surgery, if you have any questions. I'm very happy that I chose the right doctor.
I met Dr. Deniz upon the recommendation of another patient. He performed my ear surgery approximately 6 months ago with the diagnosis of Cholestatum. His care and follow-up of his patient both before and after the surgery for 6 months is commendable. I would also like to thank Dr. Deniz for his confidence in his patient and his friendly approach. I am in a much better position after the surgery, both in terms of hearing and risk of infection. I would like to thank Prof. Dr. Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz and his team.

Anesthesia Type: General

Operation Time: 2-3 Hours

Pain: Mild

Length of hospital stay: 1 night

Recovery Time 7 days
Fill in the Form
Let us call you
Take the First Step Now
For more information, contact us
Schedule your appointment or online consultation with Prof. Dr. Mustafa Deniz Yılmaz now. Take the first step in your treatment process and let’s begin your journey to recovery together with personalized solutions.














